

Pulwell’s engineering design service can assist in all technical aspects of your requirement, analyzing the optimum profile shape and all other aspects to ensure that the design is technically correct for the application.Advancement in process and composite materials technology is our ongoing goal. We continue to be innovative and invest heavily in technology research and development to ensure that our products maintain their reputation for excellence.
The Pultrusion Process
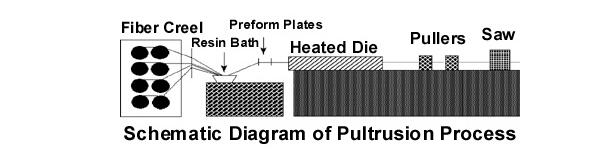
Pultrusion is a technique for the continuous manufacture of fiber reinforced composite profiles. By incorporating  glass, carbon, aramid and other high performance fibers into a range of high performance resins, physical properties can be achieved to meet the needs of engineers in a wide variety of applications. Reinforcement fibers are drawn into a resin impregnation zone and then pulled through a preformer into a heated die. Here the shape of the end product is determined by the configuration of the die and the resin is polymerized.
glass, carbon, aramid and other high performance fibers into a range of high performance resins, physical properties can be achieved to meet the needs of engineers in a wide variety of applications. Reinforcement fibers are drawn into a resin impregnation zone and then pulled through a preformer into a heated die. Here the shape of the end product is determined by the configuration of the die and the resin is polymerized.
Advantages of the pultrusion process
1.High stiffness to weight ratio--Also known as specific stiffness, it allows materials of different mass to be compared quickly in rigidity-sensitive applications where weight is still a factor. Carbon fiber does extremely well in this area, being about 3 times stiffer than steel and aluminium for a given weight.
With all the fibers running unidirectionally, pultruded tubes take optimal advantage of this characteristic.
2.High strength to weight ratio--Also known as specific strength, this is similar to the stiffness to weight ratio. This ratio allows you to compare materials of different mass for applications where resistance against breaking has priority.
3.The ability to easily make tubes with specific wall-thicknesses--The inside diameter of a pultruded tube is determined by a mandrel, which is easy to exchange for a different sized one, making it easy to produce tubes with varying wall thickness.
4. Easy to machine--Because of the low density of composites, they lend themselves to be machined well.
In short, the pultrusion process gives you a different way to solve your design challenges — one that can reduce costs and improve performance in the long run. To maximize these benefits, however, it’s best to design with the properties of FRP in mind from the start. Our engineers and fabricators can help, so contact us with your specific demand.
Contact Pulwell for more information
The Roll wrapping process
Roll-wrapping involves the applying of resin pre-impregnated composite fiber cloth (Pre-Preg) around a mandrel. The outer diameter of the mandrel thus determines the inner diameter of the final tube. The mandrel and cloth are then spiral wrapped with a consolidation tape under tension to hold the laminate in place during the curing phase. After curing, the mandrel is extracted to leave the tube ready for machining or finishing as necessary.

Advantages of the roll-wrapping process
1. Precise fiber volume fraction--The fiber comes pre-impregnated in frozen state to the tube manufacturer. Since the carbon and resin are pre-mixed in a temperature and particle controlled environment, the fiber volume fraction can be tightly controlled. This results in more consistent mechanical properties in the end product.
2. Small custom batches--The production process is relatively inexpensive and the Pre-Preg fabric can be used for many end products.
3.High degree of customization possible--The ease of adding or subtracting localized reinforcements make it possible to create custom end products to fit nearly any composite tube need.
4.Tapered tubes are possible--Since wrapping is not a continuous process but uses a mandrel of defined dimensions, a tapered profile can be build.
Contact Pulwell for more information
The Compression Molding process--SMC/BMC
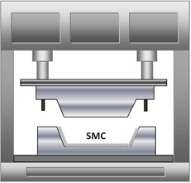 Compression molding is a closed mold process, the most common choice for high-volume composite parts and often associated with SMC and BMC materials.
Compression molding is a closed mold process, the most common choice for high-volume composite parts and often associated with SMC and BMC materials.
This process produces high strength, complex parts in a wide variety of sizes. Matched metal dies are mounted in a hydraulic molding press. The material charge is manually or robotically placed in the mold, the heated mold halves are closed, and up to 2,000psi of pressure is applied. Cycle time ranges from one to five minutes, depending on part size and thickness. Features such as ribs, bosses and inserts can be molded in.
Compression molded fiberglass parts are characterized by net size and shape, two excellent finished surfaces, and outstanding part-to-part repeatability. Trimming and finishing costs are minimal.
The advantages:
1.High Volumes
2.Excellent surface finish
3.Molding complex, high-strength large parts
4.Two finished surfaces
5.Part consistency
Sheet Moulding Compound (SMC) is a ready to mould glass-fibre reinforced polyester material primarily used in compression moulding.
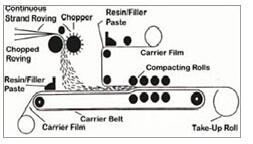 SMC is both a process and reinforced composite material. This is manufactured by dispersing long strands (usually >1”) of chopped fiber (commonly glass fibers or carbon fibers on a bath of resin (commonly polyester resin, vinylester resin or epoxy resin). The longer fibers in SMC result in better strength properties than standard bulk moulding compound (BMC) products. Typical applications include demanding electrical applications, corrosion resistant needs, structural components at low cost, automotive, and transit.
SMC is both a process and reinforced composite material. This is manufactured by dispersing long strands (usually >1”) of chopped fiber (commonly glass fibers or carbon fibers on a bath of resin (commonly polyester resin, vinylester resin or epoxy resin). The longer fibers in SMC result in better strength properties than standard bulk moulding compound (BMC) products. Typical applications include demanding electrical applications, corrosion resistant needs, structural components at low cost, automotive, and transit.
Advantages
Compared to similar methods, SMC benefits from a very high volume production ability, excellent part reproducibility, it is cost effective as low labor requirements per production level is very good and industry scrap is reduced substantially. Weight reduction, due to lower dimensional requirements and because of the ability to consolidate many parts into one, is also advantageous. The level of flexibility also exceeds many counterpart processes.
Bulk molding compound (BMC) is a ready to mold, glass-fiber reinforced thermoset polyester material primarily used in injection moulding and compression moulding.
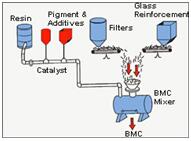 A combination of resin paste and chopped glass combined with a "sigma" blade mixer under conditions of very high mechanical "working" stress. The compound is delivered to the press in the form of a ball, slab or an extruded log and dropped into the bottom of a mould; the material is flowed outward until it assumes the shape of the mould.
A combination of resin paste and chopped glass combined with a "sigma" blade mixer under conditions of very high mechanical "working" stress. The compound is delivered to the press in the form of a ball, slab or an extruded log and dropped into the bottom of a mould; the material is flowed outward until it assumes the shape of the mould.
No.20 Lianhong Road, Torch High-Tech Industrial Zone, Zhongshan City, Guangdong 528437, PRC
Copyright © 2025 Pulwell Composites Co.,Ltd. All rights Reserved
Tel:+86-760-86133399, Fax:+86-760-86133398